반응형
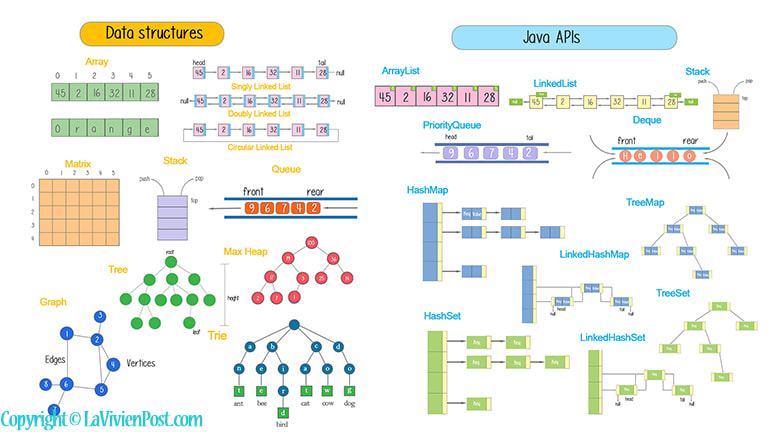
1. Array
Syntax
// Declaring and Creating Arrays
int[] nums = new int[3];
double[] dubs = {1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0};
String[] str = {"Hello", , "world!"};
int[][] arr = new int[2][5];
// length of array
int ln = nums.length;
Example
// foreach loops
public class TestArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] arrList = {2.0, 3.3, 5.5, 7.1};
// Print all the array elements
for (double element: myList) {
System.out.println(element);
}
}
}
Reference link
2. Stack
Definition
- 한쪽 끝에서 삽입과 삭제가 일어나는 구조
- 가장 나중에 삽입된 자료가 제일 먼저 삭제
Operation in Stack
- Create : 빈 스택 생성
- Empty : 스택이 비어있는지 확인
- Push : 스택에 자료 삽입
- Pop : 스택에서 자료를 하나 삭제
- Peek : 스택의 top이 가리키는 데이터를 하나 읽음 (top은 변화 없음)
Stack Overflow and Underflow
- 스택이 꽉 차 있을 때 Push 작업을 시도하면 overflow 발생
- 스택이 비어 있을 때 Pop 작업을 시도하면 underflow 발생
Examples
public class myStack {
// 1) Create : 빈 스택 생성
private Object[] stackArray; // 데이터 저장을 위한 배열 선언
private int maxSize; // 배열의 최대 사이즈
private int top; // 마디막 데이터의 위치
public myStack(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.stackArray = new Object[maxSize];
this.top = -1;
}
// 2) Empty : 스택이 비어있는지 체크
public boolean empty() {
return (top == -1);
}
// 3) Push : 스택에 자료를 삽입
public boolean full() {
return (top == maxSize - 1);
}
public void push(Object item) {
if (full())
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException((top + 1) + ">=" + maxSize);
stackArray[++top] = item;
}
// 4) Peek : 데이터 유지하면서 꺼내기 (top의 데이터 하나를 읽음)
public Object peek() {
if (empty())
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(top);
return stackArray[top];
}
// 5) Pop : 스택에서 자료를 하나 삭제
public Object pop() {
Object item = peek();
top--;
return item;
}
// 실행
public static void main(String[] args){
myStack stack = new myStack(10);
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++){
stack.push("데이터 : "+ i);
}
stack.push("데이터 : 6");
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터 : 6
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터 : 5
System.out.println(stack.peek());
// 데이터 : 4
System.out.println(stack.peek());
// 데이터 : 4
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터 : 4
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터 : 3
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터 : 2
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터 : 1
// Stack을 활용한 연산차 후치 표기법 수행
// (5_7) * 8 => 57+8*
myStack as = new myStack(15);
as.push(5);
as.push(7);
as.push((Integer)as.pop() + (Integer)as.pop());
as.push(8);
as.push(Integer.parseInt(as.pop().toString())
* Integer.parseInt(as.pop().toString()));
System.out.println(as.peek());
}
}
Java API - Stack (예제1)
// Stack API Sample
import java.util.Stack;
public class stackSample {
public static void main(String[] args){
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++){
stack.push("데이터-" + i);
}
stack.push("데이터-6");
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터-6
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터-5
System.out.println(stack.peek());
// 데이터-4
System.out.println(stack.peek());
// 데이터-4
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터-4
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터-3
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터-2
System.out.println(stack.pop());
// 데이터-1
Stack st = new Stack();
st.push("0");
st.push("1");
st.push("2");
System.out.println("=stack=");
while(!st.empty()){
System.out.println(st.pop());
// 2
// 1
// 0
}
}
}
LinkedList 이용 - Stack (예제2)
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList<String> stack = new LinkedList<String>();
stack.add("flower");
stack.add("dog");
stack.add("peope");
String s = stack.removeLast();
System.out.println(s);
int size = stack.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
System.out.println(stack.removeLast());
// people
// dog
// flower
}
3. Queue
Definition
- 한쪽 끝에서 삽입, 다른 쪽 끝에서 삭제가 일어나는 자료구조
- 가장 먼저 삽입된 자료가 제일 먼저 삭제
Operation in Queue
- Create : 빈 큐를 생성
- Empty : 큐가 비어있는지 확인
- Insert : 큐에 자료를 삽입
- Remove : 큐에서 자료를 하나 삭제
Queue overflow and underflow
- 큐가 꽉 차 있을 때 Insert 작업을 시도하면 overflow 발생
- 큐가 비어 있을 때 Remove 작업을 시도하면 underflow 발생
Examples
// 1) Create : 빈 큐를 생성
public class myQueue{
private int front;
private int rear;
private int maxSize;
private Object[] queyeArray;
public myQueue(int maxSize){
this.front = 0;
this.rear = -1;
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.queyeArray = new Object[maxSize];
}
// 2) Empty : 큐가 비어있는지 확인
public boolean empty(){
return (front == rear +1);
}
public boolean full(){
return (rear == maxSize-1);
}
// 3) Insert : 큐에 자료를 삽입
public void insert(Object item){
if(full())
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
queyeArray[++rear] = item;
}
// 4) Peek : 자료를 유지하면서
public Object peek(){
if(empty())
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
return queyeArray[front];
}
// 5) Remove : 큐에서 자료를 하나 삭제
public Object remove(){
Object item = peek();
front++;
return item;
}
// 실행
public static class QueueTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
myQueue mq = new myQueue(15);
mq.insert("Hello--");
mq.insert("Hi--");
mq.insert("JAVA");
System.out.println(mq.remove());
System.out.println(mq.remove());
System.out.println(mq.remove());
}
}
}
Java API - Queue (예제: PriorityQueue)
// PriorityQueue - Queue내의 데이터를 순서대로 정렬하여 꺼내줌
public static void main(String[] args){
PriorityQueue<Integer> intQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
intQueue.offer(30);
intQueue.offer(20);
intQueue.offer(5);
intQueue.offer(50);
intQueue.offer(40);
int len = intQueue.size();
for(int i =0; i<len ; i++){
System.out.println(intQueue.poll());
}
// 5
// 20
// 30
// 40
// 50
PriorityQueue<String> sQueue = new PriorityQueue<String>();
sQueue.offer("CDE");
sQueue.offer("ABC");
sQueue.offer("FGH");
sQueue.offer("CCE");
System.out.println(sQueue.poll());
System.out.println(sQueue.poll());
System.out.println(sQueue.poll());
sQueue.offer("CCE");
// ABC
// CCE
// CDE
// FGH
}
4. LinkedList
Deinition
- 실제 데이터인 node와 인접한 노드의 위치를 나타내는 link로 구성
- 필요에 의해 할당되는 동적인 자료구조
- 연속된 메모리의 공간이 필요하지 않음
- Type
- 단순연결 리스트
- 환형연결 리스트
- 이중연결 리스트
- 이중환형연결 리스트
장단점
- 장점: 자료의 삽입, 또는 삭제 시 데이터의 이동이 없음
- 단점
- 자료에 직접 접근할 수 없음
- 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터로 인해 그만큼의 메모리를 더 사용함
Examples
// 1) 헤더 생성
private class myLinkedList{
private Node header;
private int size;
public myLinkedList(){
header = new Node(null);
size = 0;
}
// 2) 연결할 노드 작성
private class Node{
private Object data;
private Node nextNode;
Node(Object data){
this.data = data;
this.nextNode = null;
}
}
// 3) 데이터를 저장
public void addFirst(Object data){
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.nextNode = header.nextNode;
header.nextNode = newNode;
size++;
}
public void addLast(Object data){
add(size, data);
}
public void add(Object data){
addLast(data);
}
// 4) 특정 위치에 데이터를 저장 (중간 삽입)
public void add(int index, Object data){
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
Node previous = getNode(index - 1);
Node next = previous.nextNode;
Node newNode = new Node(data);
previous.nextNode = newNode;
newNode.nextNode = next;
size++;
}
// 5) 데이터 꺼내기
public Node getNode(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);
}
Node node = header.nextNode;
for(int i=0; i <index; i++){
node = node.nextNode;
}
return node;
}
public Object get(int index){
return getNode(index).data;
}
public Object getFirst(){
return get(0);
}
// 6) 데이터 위치 탐색
public int getNodeIndex(Object data) {
if(size<=0)
return -1;
int index=0;
Node node = header.nextNode;
Object nodeData = node.data;
while(data.equals(nodeData)) {
node = node.nextNode;
if(node == null) {
return -1;
}
nodeData = node.data;
index ++;
}
return index;
}
// 7) 데이터 삭제
public Object removeFirst(){
Node firstNode = getNode(0);
header.nextNode = firstNode.nextNode;
size--;
return firstNode.data;
}
public boolean remove(Object data){
int nodeIndex = getNodeIndex(data);
if(nodeIndex == -1){
return false;
} else{
remove(nodeIndex);
return true;
}
}
public Object removeLast(){
return remove(size-1);
}
// 8) 데이터 삭제 (특정 위치)
public Object remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size){
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: "+size);
} else if(index==0){
return removeFirst();
}
Node previous = getNode(index-1);
Node removeNode = previous.nextNode;
Node next = removeNode.nextNode;
previous.nextNode = next;
size--;
return removeNode.data;
}
// 실행
public static class linkedListTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
myLinkedList ml = new myLinkedList();
ml.add("Mt.Everest");
ml.add("K2");
ml.add("Kanchenjunga");
ml.add("Lhotse");
ml.add("Makalu");
ml.add("Cho oyu");
ml.add("Dhaulagiri");
ml.add("Manaslu");
ml.add("Nanga Parbat");
ml.add("Annapurna I");
ml.add("Gasherbrum I");
ml.add("Brad Peak");
System.out.println("---- Highest Mountains ----");
for (int i=0; i<=ml.size-1; i++) {
System.out.println(ml.get(i));
}
System.out.println("---- Highest Mountains (except 3,4) ----");
ml.remove(2);
ml.remove(3);
for (int i=0; i<=ml.size-1; i++) {
System.out.println(ml.get(i));
}
System.out.println("---- Highest Mountains (except 1,3,4,12) ----");
ml.removeFirst();
ml.removeLast();
for (int i=0; i<=ml.size-1; i++) {
System.out.println(ml.get(i));
}
}
}
}
Java API - LinkedList (예제1)
public class linkedListSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
list.add(100);
list.add(200);
list.add(300);
list.add(400);
list.add(500);
System.out.println(list);
// [100, 200, 300, 400, 500]
list.add(2,300);
list.addFirst(50);
System.out.println(list);
// [50, 100, 200, 300, 300, 400, 500]
System.out.println(list.get(4));
// 300
list.remove(2);
list.remove(new Integer(400));
System.out.println(list);
// [50, 100, 300, 300, 500]
list.removeFirst();
list.removeLast();
System.out.println(list);
// [100, 300, 300]
System.out.println("size: "+list.size());
// size: 3
}
}
Java API - ArrayList (예제2)
public class arrayListSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> nums = new ArrayList<>();
nums.add(10);
nums.add(20);
nums.add(30);
nums.add(40);
System.out.println(nums);
// [10, 20, 30, 40]
nums.add(1, 50);
System.out.println(nums);
// [10, 50, 20, 30, 40]
nums.remove(2);
System.out.println(nums);
// [10, 50, 30, 40]
System.out.println(nums.get(2));
// 30
System.out.println(nums.size());
// 4
System.out.println(nums.indexOf(30));
// 2
Iterator it = nums.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
int value = (int) it.next();
if (value == 30) {
it.remove();
}
System.out.println(value);
}
System.out.println(nums);
// 10
// 50
// 30
// 40
// [10, 50, 40]
for (int value : nums) {
System.out.println(value);
}
// 10
// 50
// 40
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(nums.get(i));
}
// 10
// 50
// 40
}
}
Java API - HashMap (예제3)
public class Employee {
private String name;
private int id;
private int sal;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public int getSal() {
return sal;
}
public Employee(String name, int id, int sal) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.sal = sal;
}
}
public class mapSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
map.put("Mt.Everest", new Integer(8848));
map.put("K2", new Integer(8611));
map.put("Kanchenjunga", new Integer(8586)); // Key 중복을 허용하지 않음
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println("K2 높이는 : "+map.get("K2"));
HashMap<String, Employee> hm = new HashMap<String, Employee>();
hm.put("김수현", new Employee("김수현", 1, 3000));
hm.put("전지현", new Employee("전지현", 2, 3500));
//Employee emp = hm.get("김수현");
System.out.println(hm.get("김수현").getName() + " : " + hm.get("김수현").getSal());
System.out.println(hm.get("전지현").getName() + " : " + hm.get("전지현").getSal());
}
}5. Tree & Graph
Tree Definition
- 트리는 비선형 자료구조로 자료들 간 계층 관계를 가진 자료구조
- 용어
- Node(노드): 데이터
- Root Node(루트노드) : 시작노드
- Sibling Node(형제노드) : 형제노드
- Edge(간선) : 데이터 연결선
- 이진 트리의 분류
- 자식 노드의 차수가 2인 트리를 2진트리라 함
- 이진 트리의 종류
- 포화 이진 트리 : 모든 레벨의 노드과 꽉 차서 포화 상태인 이진 트리
- 완전 이진 트리 : 높이(h), 노드수(n) - h-1은 포화 이진트리이고 마지막 레벨이 가득 차있지 않은 트리
- 편향 트리 : 왼쪽이나 오른쪽으로 치우친 이진 트리
- 트리의 순회
- 전위 순회 : DLR로 순회
- D: 현재 노드 n 을 방문
- L: 현재 노드 n의 왼쪽 서브 트리로 이동
- R: 현재 노드 n의 오른쪽 서브 트리로 이동
- 중위 순회 : LDR로 순회
- L: 현재 노드 n의 왼쪽 서브 트리로 이동
- D: 현재 노드 n을 방문
- R: 현재 노드 n의 오른쪽 서브 트리로 이동
- 후위 순회 : LRD로 순회
- L: 현재 노드 n의 왼쪽 서브 트리로 이동
- R: 현재 노드 n의 오른쪽 서브 트리로 이동
- D: 현재 노드 n을 방문
- 전위 순회 : DLR로 순회
Graph Definition
- 연결되어 있는 데이터의 관계를 표현하는 구조
- 용어
- 정점(Vertex) : 그래프를 구성하는 객체(데이터)
- 간선(Edge) : 정점을 연결하는 선
- Graph Search (그래프 탐색 방법)
- 깊이 우선 탐색 (DFS: Depth First Search)
- Stack 을 이용하여 탐색
- 무작정 막힐때까지 탐색하고, 막히면 다시
- 너비 우선 탐색 (BFS: Breadth First Search)
- Queue를 이용하여 탐색
- 너비 우선 탐색은 깊이가 1인 모든 정점을 방문하고, 깊이가 2인 모든 정점을 방문하고, 깊이가 3인 모든 정점을 탐색하는 방법으로 탐색
- DFS보다 조금 더 효과적임
- 재귀 호출을 사용하지 않아서 Stack OverFlow가 발생하는 것을 막을 수 있음
- 깊이 우선 탐색 (DFS: Depth First Search)
BFS 탐색 순서
- 가장 가까운 정점부터 방문
- 방문한 정점을 Queue에 저장
- Queue에서 정점 하나를 꺼내고 그 정점에서 갈 수 있는 정점들을 Queue에 저장
- 반복처리하면서 가장 먼 정점까지 방문
최소 비용 신장 트리
- 신장트리(Spanning Tree) : N개의 정점과 n-1개의 간선으로 만들어진 트리
- 최소 비용 신장 트리
- 그래프의 간선에 비용이나 거리, 시간 등의 가중치가 부여될 수 있음
- 무방향 가중치 그래프에서 최소의 가중치 합으로 탐색할 수 있는 그래프
- 최소 비용 신장 트리를 만들기 위한 알고리즘
- Kruskal 알고리즘 I
- Kruskal 알고리즘 II
- Prime 알고리즘
반응형
'Biusiness Insight > Computer Science' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Google Cloud Summit Seoul 2024 참관 (0) | 2024.07.28 |
|---|---|
| Google I/O 2023 키노트 요약 (0) | 2023.05.14 |
| [Java] 자바 형 변환 예제 (Type Cast Examples) (1) | 2021.08.23 |
| 메타버스 (Metaverse) 기본 개념 (1) | 2021.06.12 |
| [AWS] 아마존 S3 예제 (Amazon S3, Simple Storage Service) (0) | 2021.05.20 |



